Basic concepts of social network analysis. Connection diagram: programs for creating connections Program for building connections
The method is also called “Connection Graph”. ()
The dependency diagram is one of the seven quality management tools. The method is based on the formation of cause-and-effect relationships between certain blocks of information.
Purpose and goals
The method is used to systematize a large amount of interrelated information.
The purpose of the method is to determine the logical connections between factors influencing the occurrence of problems and the distribution of efforts in accordance with the expected effectiveness of the impact.
A link diagram is similar in purpose to an Ishikawa cause-and-effect diagram.
The essence of the method
A dependency diagram is a quality tool that allows you to build reasonable connections between the main idea, emerging problems and factors that influence the implementation of the idea.
The relationship graph helps in identifying unresolved problems in the process of action planning by visually representing the cause-and-effect relationships between information blocks.
Diagram construction procedure
The technique for constructing a relationship diagram is similar to constructing an affinity diagram:
- A meeting of specialists necessary to resolve issues is organized;
- The formulation of the problem or desired result is determined;
- Information blocks describing influencing factors are highlighted, information is recorded on cards;
- A card with the main topic is placed in the center of the sheet, next to it are the main factors influencing the result;
- The links are connected by arrows indicating cause-and-effect relationships;
- The number of arrows directed to each event and emanating from each block is counted;
- Events that lead in the number of outgoing arrows are called initial - they are the ones that are emphasized when solving problems.
Figure 1 - Connection diagram diagram.
Identify events that are noticeably different from each other. Given the similarity of information blocks, it is difficult to determine the original event.
When constructing a diagram, use only one-way arrows.
Advantages of the method
Ease of construction and use, visual presentation of data.
Disadvantages of the method
The method is not suitable for analytical work with complex technological processes.
Examples
Figure 2 - Dependency diagram to solve the problem of lack of understanding by enterprise employees of the importance of continuous quality improvement.
Programs for constructing a circuit diagram
FreeMind is a free program that allows you to create a dependency diagram with a branched structure and links.
MS Visio is a diagram and flowchart editor for Windows.
Nowadays, every designer and programmer is faced with the construction of various kinds of diagrams and flowcharts. When information Technology have never occupied such an important part of our lives, drawing these structures had to be done on a sheet of paper. Fortunately, all these steps are now performed using automated software installed on the user's computer.
It's pretty easy to find on the internet great amount editors that provide the ability to create, edit and export algorithmic and business graphics. However, it is not always easy to figure out which application is needed in a particular case.
Due to its versatility, the product from Microsoft can be useful both to professionals who have been building various structures for many years, and to ordinary users who need to draw a simple diagram.

Like any other program in the series Microsoft Office, Visio has all the tools necessary for comfortable work: creating, editing, connecting and changing additional properties of shapes. A special analysis of the already built system was also implemented.
Dia
In second place in this list, quite rightly, is Dia, which contains all the functions necessary for a modern user for constructing circuits. In addition, the editor is distributed free of charge, which simplifies its use for educational purposes.

Huge standard library of shapes and relationships, as well as unique opportunities, not offered by modern analogues - this awaits the user when accessing Dia.
Flying Logic
If you are looking for software with which you can quickly and easily build the necessary circuit, then the Flying Logic program is exactly what you need. There is no cumbersome complex interface and a huge number of visual chart settings. One click - adding a new object, the second - creating a union with other blocks. You can also combine schema elements into groups.

Unlike its analogues, this editor does not have a large number of different forms and connections. Plus, it is possible to display additional information on blocks, which is described in detail in the review on our website.
BreezeTree Software FlowBreeze
FlowBreeze is not separate program, and an independent module that connects to Microsoft Excel, greatly facilitating the development of diagrams, flowcharts and other infographics.

Of course, FlowBreeze is software mostly intended for professional designers and the like, who understand all the intricacies of the functionality and understand what they are paying money for. It will be extremely difficult for average users to understand the editor, especially considering the interface is in English.
Edraw MAX
Like the previous editor, Edraw MAX is a product for advanced users who are professionally involved in such activities. However, unlike FlowBreeze, it is self-contained software with countless possibilities.

In terms of interface style and operation, Edraw is very similar to Microsoft Visio. It’s not for nothing that it is called the latter’s main competitor.
AFCE Algorithm Flowcharts Editor
This editor is one of the least common among those presented in this article. This is due to the fact that its developer - an ordinary teacher from Russia - completely abandoned the development. But his product is still in some demand today, since it is perfect for any schoolchild or student who is learning the basics of programming.

In addition to this, the program is completely free, and its interface is made exclusively in Russian.
FCEditor
The concept of the FCEditor program is radically different from others presented in this article. Firstly, the work occurs exclusively with algorithmic flowcharts, which are actively used in programming.

Secondly, the FSEditor independently, in automatic mode builds all the structures. All the user needs is to import the ready-made source in one of the available programming languages, and then export the code converted into a diagram.
BlockShem
The BlockShem program, unfortunately, provides much fewer functions and conveniences for users. There is no automation of the process in any form. In Flowchart, the user must manually draw the shapes and then combine them. This editor is more of a graphical editor than an object editor intended for creating diagrams.

Unfortunately, the library of figures in this program is extremely poor.
As you can see, there is a large selection of software designed for creating flowcharts. Moreover, applications differ not only in the number of functions - some of them imply a fundamentally different operating principle, distinguishable from analogues. Therefore, it is difficult to advise which editor to use - everyone can choose exactly the product that they need.
Connection diagram(thought map, associative map, mind map) - this is a great way to “sort out” thoughts, ideas, facts, concepts, tasks. Nowadays such diagrams are actively used in study and work. To create them, you can use a pen and a piece of paper the old fashioned way, or you can use special software.
A mind diagram is used in the learning process, for example, to create notes or organize material on a specific topic. You can also use it for solving creative problems, brainstorming, or creating presentations. A mind diagram will help you organize things or plan a specific project.. Finally, it can even be used to solve personal problems.
A mind diagram created manually helps you better understand the material or understand yourself (if you use this technique to solve personal problems). But if you need to present a finished diagram at work or school, it will look much more solid mind diagram created in special program . In addition, this will save you from having to carry around a rather large piece of paper that can get wrinkled: you put the diagram on a flash drive and that’s it.
There are many free programs to create mind maps. Perhaps one of the most famous is FreeMind. This is a cross-platform application written in Java and distributed under the GNU GPL license. With XHTML export, you can create complex diagrammatic maps that contain links to external sources (other mind maps, files, and web pages).
The program allows you to hide individual branches, use HTML to format nodes, decorate corners and branches, graphically link nodes, search for individual branches, import and export lists. The finished mind diagram can be exported to JPEG, PNG, SVG and PDF formats. Provided integration of the application with wiki projects.
Based on the FreeMind application, two more projects were created: FreePlane and SciPlore MindMapping. In a programme FreePlanе the emphasis was on ease of use. One of the key developers of FreeMind took part in its creation. Like its “parent”, this program is cross-platform. It fully supports the FreeMind file format, but also contains additional options and features not supported by FreeMind.
Program SciPlore MindMapping more aimed at students and scientists. It places greater emphasis on working with PDF format(including import of bookmarks) and support for BibTeX keys (software for creating formatted bibliography lists). This is the first program that combines the creation of link diagrams and the management of bibliographic information. The SciPlore MindMapping file format is 100% compatible with FreeMind.
Based on FreeMind WikkaWiki(often called simply Wikka). Essentially, this is a wiki engine written in PHP that uses the MySQL DBMS to store pages. The engine is very light and efficient, it combines standard features wiki engine with support for FreeMind memory cards.
Project VUE (Visual Understanding Environment) was created specifically for educational institutions and is distributed under an appropriate license. It's cross platform free application can also be used to create presentations. In addition to the standard options found in most mind mapping applications, VUE boasts new features: tools for dynamic map presentation, tools for merging and analyzing maps, advanced keyword tagging and search capabilities, support for the semantic web, advanced search on online resources (Flickr, Twitter, Yahoo, etc.).
Program XMind It has a fairly simple interface. It is used for task and knowledge management, in meetings and in time management. A mind diagram created in this application can contain element boundaries, relationships between elements, labels, bullets, links, text annotations, audio and graphic files, attached files of other formats. Finished documents can be exported to PowerPoint, MS Word and PDF.
Another free program for creating circuit diagrams can be mentioned CAM editor, Compendium, Pimki. There are also websites for creating mind maps. Most of these services are shareware. This means that you can either create only a limited number of cards in free mode (usually 2-3), or use the service for free for a limited amount of time (about a week).
A mind diagram can become an indispensable assistant in study and work, and if you choose the right program, its creation will not be difficult for you!

Everyone knows that for the successful development of a website/web service/program (underline as appropriate), the design stage is very important. A competent development plan is half of the entire project. It is clear that first of all, a technical specification is needed, which will describe the requirements, deadlines, etc. But it is even more important visual design, namely: UML diagrams, database diagrams, user interfaces, page thumbnails...
To solve each of these problems there are own means.
For example, user interfaces can be depicted on paper or in Photoshop. But, you must admit that it would be much more convenient to be able to create all of the above in one program.
Below I offer an overview of several such programs with a brief summary. I really hope to see in the comments links to other software that allows you to perform such complex visual design.
Microsoft Visio
License: TrialPrice: 18,000 rub.
Website: http://office.microsoft.com/ru-ru/visio/
MS Visio 2007 is a universal tool for creating diagrams, graphs, and diagrams of any kind. Includes powerful visualization tools and is suitable for a wide range of tasks.
Open Office.org Draw
License: FreeWarePrice: free
Website: www.openoffice.org/product/draw.html
Although OO Draw is a vector graphics editor, many people use it to draw drawings, flowcharts and other types of diagrams.
Axure RP Pro
License: TrialPrice: $585
Website: http://axure.com
Axure is designed for creating and quickly prototyping website wireframes. The interface is similar to MS Visio. Contains a very large library with a set of objects for page design and user interfaces. Allows you not only to create a graphical representation, but also to bind events, link blocks together and much more. Wide range of possibilities for exporting a finished diagram.
SmartDraw 2009
License: TrialPrice: $197
Website: http://www.smartdraw.com/
A very powerful tool that allows you to create all possible types of interfaces. The interface is similar to MS Office 2007. A giant library of objects (additional elements are available on the official website), and all kinds of diagram types.
Gliffy.com
License: ShareWarePrice:$5 per month
Website: http://www.gliffy.com/
Gliffy.com is a web application written in Flash. Has in its arsenal tools for creating flowcharts, structures, user interfaces, uml diagrams. Provides convenient publishing tools and joint development documents. It is possible to import both raster and vector graphics. IN free version There is a limit on the maximum number of documents - 5.
SNA (Social network analysis - analysis social networks) is a direction of modern computer sociology that deals with the description and analysis of connections (networks) of varying density and intensity that arise during social interaction and communication. The behavior of an individual is a derivative of the social networks of which it is an element. SNA method received wide use when studying communication processes in various social groups, in the development of scientific schools, sociology of interpersonal relationships, political and international processes, etc. A network of social interactions is a network consisting of so-called social actors (actor - from the English actor (actor, personality) - the term is used in Russian-language literature and has a broader meaning than the Russian word "person", that is, it may not be only human or entity, but also a set of organizations or an entire country) and sets of relationships between them. The research method is universal. Not only individuals can act as social actors, but also social groups, organizations, cities and countries. Connections are understood not only as communication interactions between actors, but also as connections for the exchange of various resources, interactions associated with joint activities, including conflict relations. When using the SNA method, the key is to describe the characteristics that express the density, intensity and spatial coordination of social connections, which makes it possible to identify structural units of research (“nodes”, “blocks”, “cliques”, “bushes”) in the system of social relations.
The resulting network of interactions can be analyzed various methods graph theory, information theory, mathematical statistics. Unlike classical methods of analysis, which examine the individual properties of objects, the main goals of network analysis are to study the interaction between social objects (actors) and identify the conditions for the emergence of this interaction.
A separate area of research is visualization (graphical display of a social network). Visualization is important because the very ability to see the network allows one to draw important conclusions about the nature of the interaction of actors, without resorting to other methods of graph analysis. To explain this thesis, it is advisable to give an example of using the SNA method to identify terrorists who planned the terrorist attack of September 11, 2001 in the United States (Fig. 1). In this work, a network was built in which specific individuals (pilots) acted as actors (vertices), and facts of pairwise connections (negotiations) acted as communication lines (edges). The fact that the terrorists were preparing a terrorist attack (they had excessive communications against the general background) is clearly visible from the thickening of the density of communication lines around the terrorists.
Rice. 1. An example of a study of terrorist interactions
during the planning and implementation of the terrorist attack of September 11, 2001 in the United States.
Designations on the graph: points - pilots, connections between points - intensity of communications between these individuals.
Flight numbers are indicated in color:

After becoming familiar with SNA technology, the author of the article had the idea to build and visually present a social network that displays the interactions of the most important historical figures in Russian history. In the process of completing this project, I had to work with a number of programs for building social networks. The experience gained allowed me to write this article. Some of the programs described below can be downloaded from the CD included with the magazine.
A brief overview of programs for visualizing social networks
Programs for constructing graphs can be divided into two categories: the first are editors - applications that allow you to automate the manual construction of a graph and provide the ability to automatically change edges when moving graph vertices; the second group is programs that allow you to abandon manual drawing of the graph. In this case, the user specifies a certain database, from which the program calculates the position of vertices and faces and builds a graph. To construct sociograms, programs of both types can be used, since for specific cases one or another program may be the most suitable.
Programs for manual drawing of sociograms
udraw(Graph) 3.1.1
Draw graphs using graphic editors wide profile, not always convenient. It is much more effective to use specialized applications. One of these specialized programs is uDraw (Graph), which automates the process of constructing graphs and diagrams (Fig. 2).

Rice. 2. Example of constructing a diagram in uDraw (Graph)
A very convenient function of the program is the ability to deform the graph, when when you move one of the vertices of the graph (in Fig. 3, the top vertex is moved to the right), all the others are deformed automatically. Therefore, if you need to allocate space for new vertices, you do not have to redraw the mesh again.

Rice. 3. An example of transforming a uDraw (Graph) diagram in drag&drop mode
The program allows you not only to generate boxes of different shapes, but also to insert raster images as graph vertices (Fig. 4).

Rice. 4. Example of use raster images in uDraw (Graph)
More information about the program can be found at: http://www.informatik.uni-bremen.de/uDrawGraph/en/uDrawGraph/gedit.html.
Visio 2003
A very convenient tool for manually constructing graphs is the Visio 2003 program (Fig. 5), which contains tools for constructing graphs and diagrams necessary for a wide range of users. It is possible to easily move individual boxes so that the lines connecting this box with others are deformed. The program allows you to save a Visio diagram in web format. The interface of web pages created in Visio is attractive and provides ample opportunities for collaboration with data both within the organization and outside it.

Rice. 5. Building a graph in Visio 2003
Programs for automatic construction of sociograms
It is obvious that manually constructing a graph is a very lengthy and labor-intensive process. Analyzing the structure of a graph consisting of hundreds of vertices is simply impossible with manual construction. Here you need to pay attention to automated systems. They made it possible to visualize complex social networks and visually analyze structures containing hundreds and thousands of vertices. One of the first works in the field of automatic construction of sociograms - the SOCK program - was carried out in 1970 (authors: Alba, Gutmann and Kadushin). This program made it possible to automatically build a graph (sociogram) based on text source data. In Fig. Figure 6 shows an example of using the program to analyze American intellectual circles.

Rice. 6. Computer sociogram of American intellectual circles
An interesting feature of the work was that subgroups were analyzed based on the graph. In Fig. 6 they are shown in the form of isolines that unite the peaks (people) according to a certain profile: “literary intelligentsia”, “biologists”, “writers and sociologists”, etc. In this way, it was possible to analyze the intersection of sets of people who have one profession or another, have certain political beliefs, etc.
After this work, carried out in the early 1970s, research was carried out for several years, aimed primarily at analyzing networks, and little work was done directly on visualization.
NEGOPY
In 1978, Lesniak and a number of other authors proposed the NEGOPY program (http://www.sfu.ca/~richards/negopy.htm), which provided graphical visualization of networks. The program has become widespread. Today NEGOPY is one of oldest programs for analyzing social networks, for searching for connections in groups, so-called cliques and isolated groups in networks with up to a thousand members and 20 thousand connections. The program is used in more than 100 universities and research centers around the world.
The main goal of the application is to highlight areas in which there are more contacts with each other than with nodes belonging to other clusters (Fig. 7). These clusters are called groups and are conceptually close in meaning to the term “cliques”, often used in sociometric literature. NEGOPY also allows nodes to be sorted into a limited set of role categories.

Rice. 7. The main goal of the program is to highlight subgroups (cliques)
NEGOPY takes as input a list of pairs that have a relationship. Links are defined by assigning ID numbers to individuals connected by links, and in addition, a number is specified that determines the strength of this link. The program allows you to take into account directed or undirected connections.
You can order the program at: [email protected]. A PDF copy of the user manual is located at: http://www.sfu.ca/~richards/Pdf-ZipFiles/negman98.pdf.
View_Net II
The View_Net II program (author - Klovdahl) was written for the Silicon Graphics platform and was intended for visualization and analysis of large databases. This application for the first time allowed to construct a three-dimensional image of a social network. The work was pioneering in its integration of visual and numerical graph analysis.
In Fig. Figure 8 shows the result of the View_Net II program. The picture shows interactions between students who studied with the program's developer in 1989 in Canberra, Australia.

Rice. 8. Visualization of social connections among students based on the View_Net II program
MultiNet
MultiNet is a program that allows you to analyze research data presented in the form of social or other networks . MultiNet is interactive program, which allows you to obtain both a numerical analysis of the source data representing a certain graph, and a visual representation of the network. The use of color and interactivity is an innovative element implemented in MultiNet. The program allows you to find the positions of vertices, represent the social network in the form of two- and 3D images, as well as manipulate the object (rotate the network in three-dimensional representation and change the color of the vertices). Rice. 9 indicates that the program allows you to visualize truly complex systems.

MultiNet was created from the very beginning as an application for analyzing large amounts of information and therefore uses special compact data storage formats and special calculation schemes optimized for analyzing large amounts of data. Detailed information about the program can be found at: http://www.sfu.ca/%7Erichards/Papers/DissAJS.pdf.
Spring Embedder
Spring embedder is a Java program developed by students at the University of Illinois for analyzing and visualizing social networks.

Rice. 10. An example of the Spring Embedder program
As can be seen from the above review, there are quite a lot of programs for constructing sociograms, but we chose the NetDraw program, which we will talk about in more detail.
NetDraw
NetDraw is a free application written by Steve Borgatti for visualizing social networks. You can download the program at: http://www.analytictech.com/Netdraw/netdraw_versions.htm or download it from the CD-ROM included with the magazine.
To enter data, the so-called DL protocol is used, which includes several formats: nodelist (node list), edgelist (edge list) and fullmatrix (matrix notation).
Nodelist format
This format is very simple. You need to create text file, for which anyone is suitable text editor. Let's look at a specific example:
format = nodelist
D.L. at the beginning of the list indicates the file type; n = 50 tells the program that 50 nodes are expected; format = nodelist means that nodelist format is expected; data: shows the beginning of the actual data in the record.
First line (1 7 8 2) indicates that the person 1 has connections with three people who are identified as 7, 8 And 2 . Second line (3 19 21 49 6) indicates that the person 3 has connections with four people, identified as 19, 21, 49 And 6 .
Edgelist format
This data entry format is useful when pairing information is available. Let's look at a specific example:
format = edgelist
N=4- these are four nodes, first line (ROMUL AMBROSE 1) says that ROMUL And AMBROSE 1 have a connection, etc. In Fig. 11 shows a sociogram corresponding this example, and in Fig. 12 - a network that already has 18 nodes.

Rice. 11. Displaying directed connections in NetDraw (4 nodes)
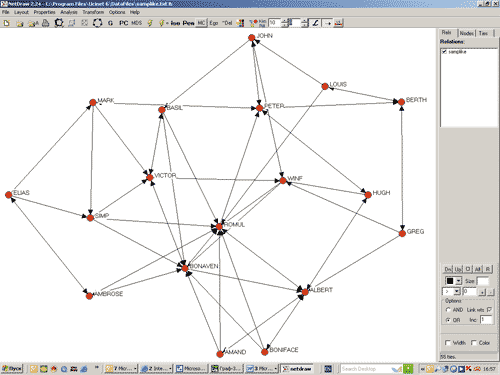
Rice. 12. Displaying directed connections in NetDraw (18 nodes)
FullMatrix format
This format is useful for small data sets that contain many relationships. To prepare the data, you can use any text editor or Excel (don't forget to save the file as a text file). The data should be presented as follows:
format = fullmatrix
Line format = fullmatrix indicates the format type. After the pointer data: The data follows in the form of a person-by-person table. Since we have five nodes (n=5), the matrix must have five rows and five columns. First line (0, 0, 1, 0, 0) shows that the person 1 has a connection with the person 3 . The second line shows that the person 2 has connections with people 4 And 5 .
Non-numeric marks can be inserted when indexing labels embedded in the following form:
format = fullmatrix
Bill Jan Jim Sue Zoe
Project “Historical Figures as a Social Network”
The goal of this project was to develop a sociogram of the most significant historical figures of Russian history.
Data collection
Historical Internet resources were used to construct the graph. By using search queries like " N was part of the inner circle M», « N met M», « N corresponded with M" etc. a database of significant interactions between historical figures and brief descriptions interaction data. The types of interactions were divided into five categories:
- family and marriage ties (undirected connection).
- mentoring (one was a student of the other) (directed communication).
- friends or associates (undirected communication).
- conflictual relationships (undirected communication).
- one was a direct or indirect cause of the death of the other (directional relationship).
Planning the graph structure

Rice. 13. Fragment of a graph obtained using the NetDraw program
The program allows you to create a structure with an optimal arrangement of nodes, transform the graph (Fig. 14), drag individual nodes manually and view a three-dimensional representation of the graph (Fig. 15 and 16).

Rice. 14. Graph restructuring capabilities (NetDraw)

Rice. 15. Possibilities of 3D representation of a graph (NetDraw)

Rice. 16. Possibilities for manipulating a 3D graph model (NetDraw)
Creating a visual sociogram
The NetDraw program allows you to plan and display the structure of a graph with a small number of elements - with large quantities elements visibility decreases. Get a visual diagram of a large social network on which you can draw boxes different color and connections (edges) of different thicknesses, we were unable to do so in the Netdraw program. Using NetDraw to construct individual fragments of the graph, we later moved on to manually constructing the graph using the Visio program (Fig. 17).

Rice. 17. Fragment of a graph in Visio
Creating an interactive web version of the sociogram
It should be noted that, despite all the clarity, a graphical representation of a social network is not convenient for study until it is equipped with an interactive help system. It is much more convenient to consider a network, where by clicking on any element (vertex, face), you can get help.
To create an interactive web version, we converted the graph into a Flash program. As a tool for developing interactive applications, Flash offers many benefits, allowing you to quickly create interactive buttons and pull-down menus with minimal programming.
As a result, an interactive version of the graph was created (only a fragment for now), in which all vertices and edges (when clicked on with the mouse) call up a help window about a particular historical figure or about events that reveal the essence of interaction in a couple.
As an example in Fig. Figure 18 shows a fragment of a graph with an illustration of interactive help about the interaction in the pair “Catherine II - Potemkin”, and in Fig. 19 - “Catherine II - Paul I.”

Rice. 18. Fragment of a graph with an illustration of a communication certificate (Catherine II - Potemkin)

Rice. 19. Fragment of a graph with an illustration of a communication certificate (Catherine II - Paul I)
The resulting graph serves as both a sociogram and an interactive interface for viewing a database of historical figures and their interactions.
In this form, the graph can be used as a guide in which you can analyze various social subgroups, obtain information on individuals and, most importantly, on connections in couples. The project is under development; a fragment of the graph in the Flash version can be viewed on the CD-ROM included with the magazine. Upon completion of the work, it is planned to create a website and, possibly, an encyclopedic multimedia disk. Given the scale of the project, the authors are interested in involving co-executors in the work. The authors would appreciate comments, which can be sent to:
